Human CD106/sVCAM-1 Precoated ELISA Kit
$499.00
Out of stock
In-stock products will arrive in 1 to 2 business days
Key Features
✓ Assay Range: 0.25-16 ng/mL
✓ Sensitivity: 0.1 ng/mL
✓ Sample Types: Serum, Plasma, Cell Culture Supernates
Size
✓ 1 Kit (96 well plate)
Need Help Ordering?
Product Details
Storage & Preparation
Data Images
Background
Product Documents
Product Details
| Product Type | Quantitative ELISA, Colorimetric |
| Product Summary |
|
| Reactivity | Human CD106/sVCAM-1
|
| Product Components |
|
Storage & Preparation
| Shipping | Shipped on blue ice |
| Stability & Storage | Store the unopened kit at 2-8℃, The kit is stable for 12 months. Do not use beyond expiration date. |
| Reconstitution | See Datasheet for Component Preparation |
Data Images
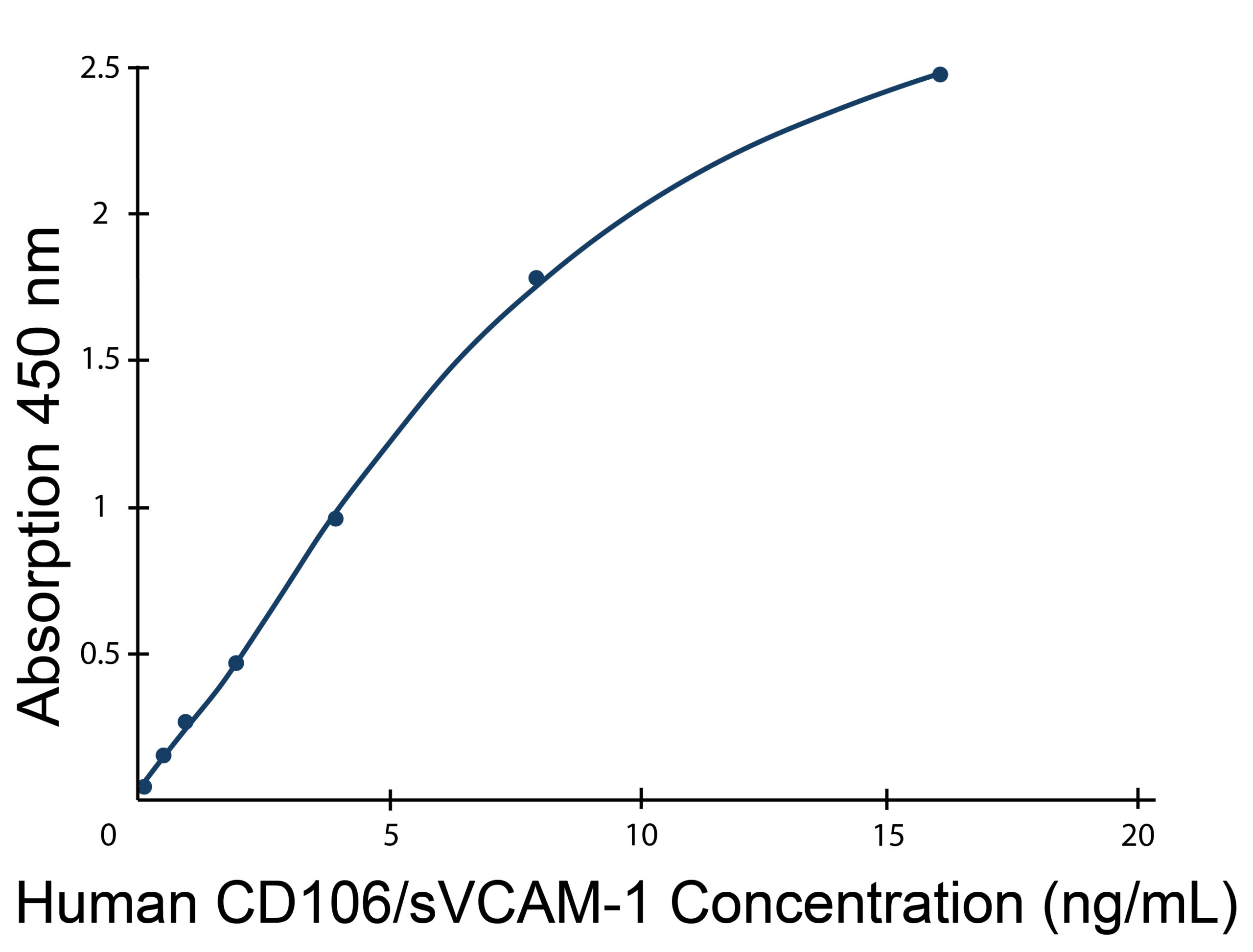
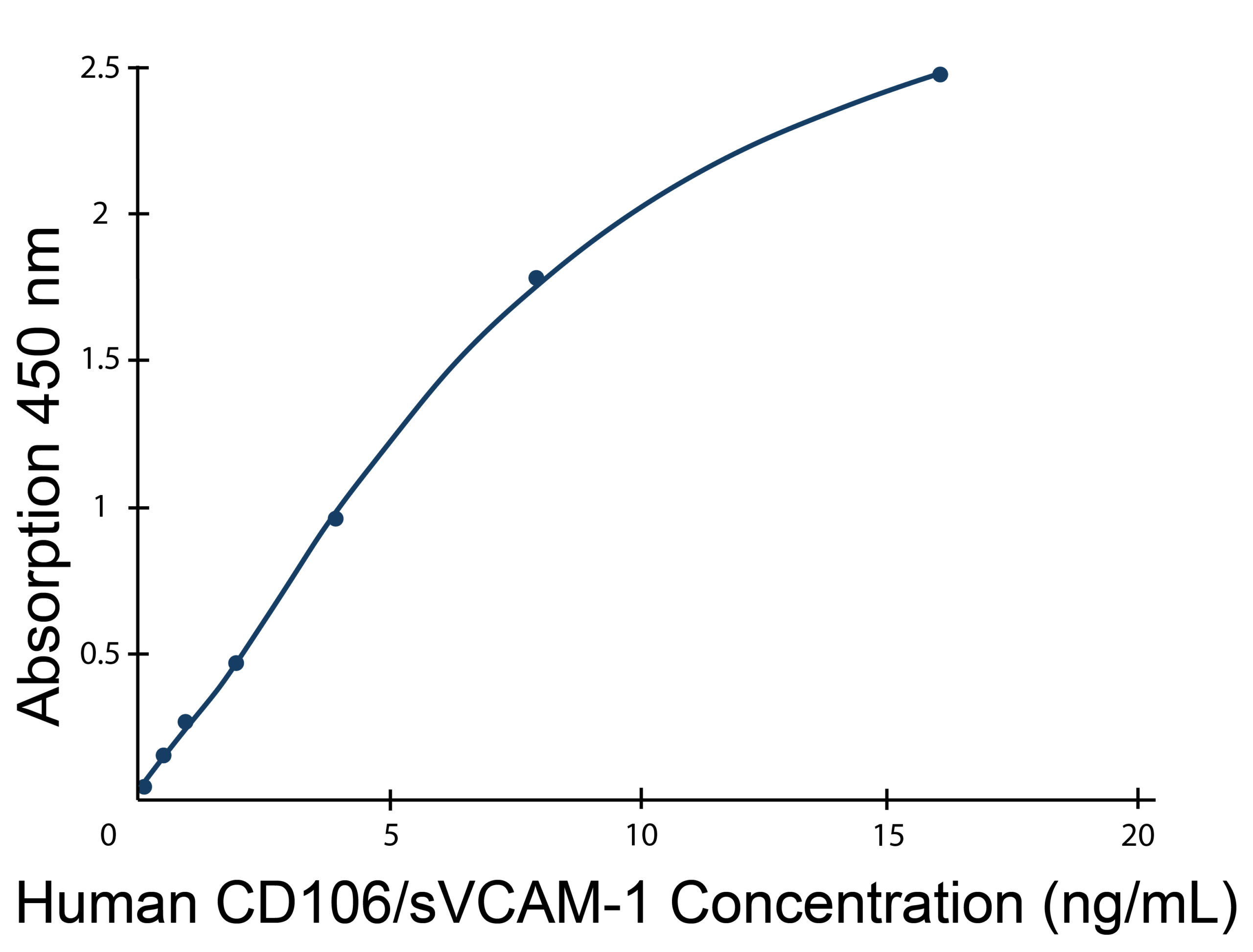
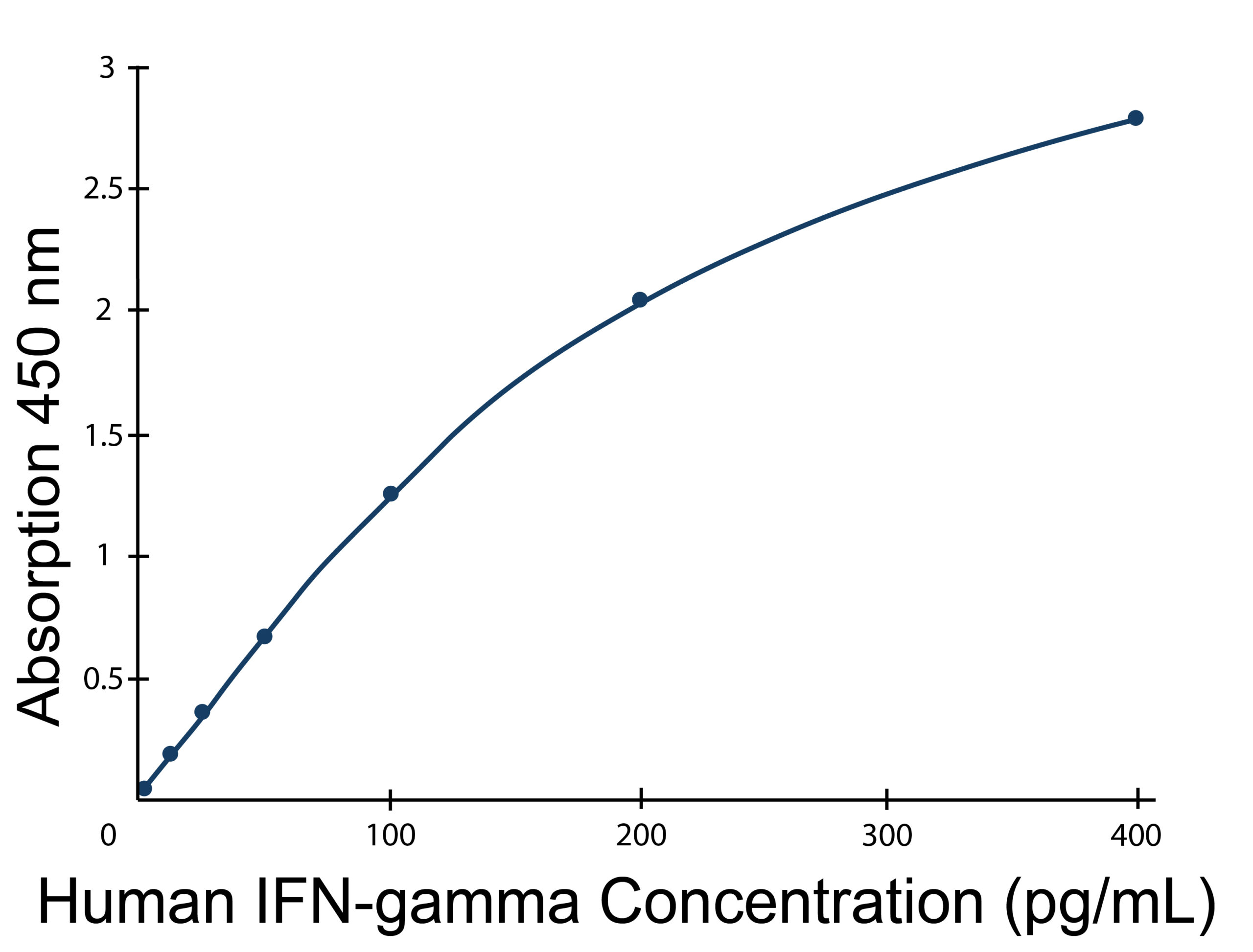
Human CD106/sVCAM-1 ELISA standard curve, typical data. User-generated standard curve is required for each set of samples. Please refer to protocol.
Background
| Alternative Names | Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1, CD106, INCAM-100 |
| Function | VCAM-1 (CD106) mediates immune cell binding, trafficking, and surveillance, crucial for leukocyte signaling and endothelial responses. VCAM-1 is upregulated in endothelial cells in response to proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, IFN-γ). The extracellular region contains seven Ig-like domains, which are critical for its adhesive functions. These domains provide binding sites for integrins, most notably the α4β1 integrin (also known as VLA-4), found on the surface of leukocytes, particularly monocytes and lymphocytes. The primary receptor for VCAM-1 is the integrin α4β1 on leukocytes, initiating outside-in signaling cascades within the leukocytes. These signals can activate various kinases, including focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and members of the MAP kinase family, which modulate cytoskeletal rearrangements and cell migration.
Soluble VCAM-1 (sVCAM-1) is a circulating form of the vascular cell adhesion molecule‐1 that plays a distinct role in modulating inflammation and immune cell trafficking. It is derived mainly from proteolytic cleavage of the membrane-bound VCAM-1. sVCAM-1 can act as a decoy receptor by binding to integrins (especially α4β1) on leukocytes. Although sVCAM-1 lacks the intracellular domain necessary for initiating signals within endothelial cells, its interaction with leukocyte integrins can still trigger outside-in signaling cascades. |
| Tissue Specificity | VCAM-1 is most prominently expressed on vascular endothelial cells. Under basal conditions, expression is generally low; however, it is markedly upregulated in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IFN-gamma) during inflammation, infection, or tissue injury: atherosclerosis, neuroinflammation, as well as lung and kidney inflammation. sVCAM-1 is reported circulating in blood during inflammatory, cardiovascular and autoimmune diseases. |
| Cellular Localization | Membrane-bound and cleaved soluble protein forms |
| Involvement in Disease | Dysregulation of VCAM-1 and its soluble form, sVCAM-1, is reported in cardiovascular, autoimmune, neuroinflammatory, pulmonary disease states, as well as cancer (tumor microenvironment, cancer cell migration, recruitment of immune cells). |
| UniProt | P19320 |
| Gene Symbol | VCAM1 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 7412 |
Product Documents
| Product Datasheet | Download Product Datasheet |
| COA | Contact Us |
| SDS | Contact Us |
You may also be interested in related products:
Reviews (no reviews yet)
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.